Deep dive into 2D arrays.
Two Dimensional arrays can be defined as arrays inside an array. The elements in a 2D array can be defined as rows and columns. You can think of 2D arrays as N x M matrix.
2D arrays are created to implement a relational database lookalike data structure. It provides ease of holding the bulk of data at once which can be passed to any number of functions wherever required.
Some examples of 2D arrays are periodic table, movie ratings by multiple ratings on multiple movies, etc.
When do you need 2D arrays?
These are some scenarios where 2D arrays are implemented:
- Digital images.
- Board games (Chess, Tic Tac Toe, Checkers).
- Many games use 2D arrays to plot visual environment of a game.
Anatomy of a 2D array
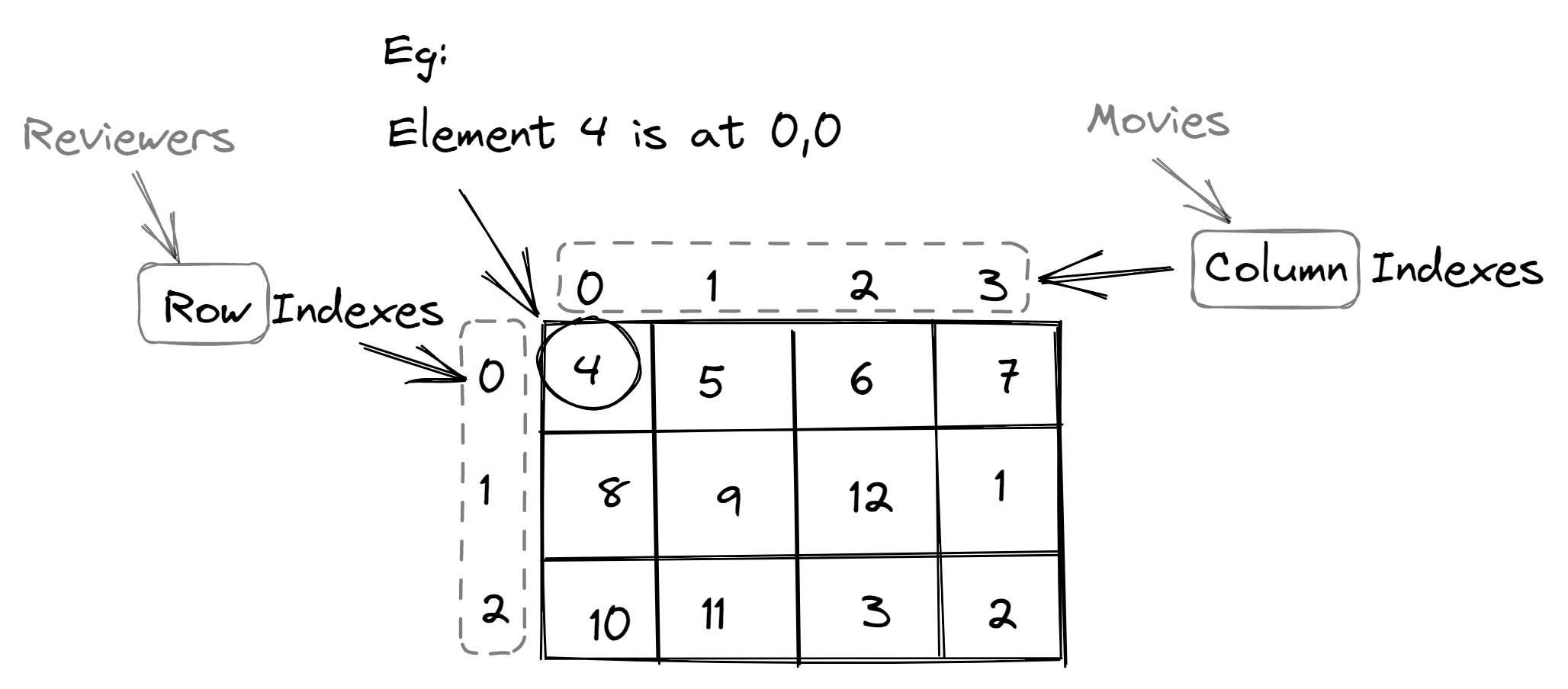 Let’s take an example of a movie rating system where you will store movies as columns and reviewers as rows:
Let’s take an example of a movie rating system where you will store movies as columns and reviewers as rows:
- There are N rows and M columns in a 2D array.
- Each row is a different reviewer and each column is a different movie, also you can see the indexing starts at 0.
- The reviewer at the 0th index has given a rating of 4 to the Movie at the 0th index.
- To get 4 from the array we write - ratings[0][0] where ratings is the array, the first subscript is a row and the second subscript is a column.
- Similarly, to get 12 from the same array we can write - ratings[1][2]
Creating 1D array vs 2D array
As a programmer, I believe you’ve already came across One-Dimensional arrays. We can create 1D array like:
# In python, we can use list to represent array.
# List index also start with 0
array = [1, 2, 3, 4]
print(array[0]) # Output: 1
Now, let’s see how we can create 2D array:
# In python, we can use list[[],[]] (list of lists) to represent 2D array.
ratings = [[4, 5, 6, 7], [8, 9, 12, 1], [10, 11, 3, 2]]
print(ratings[0][0]) # Output: 4
To find the length of a 2D array generally, we consider the number of rows present in it:
# To find length of an array will use len() method.
print(len(ratings)) # Output: 3
Iterate over elements of a 2D array:
for i in range(len(ratings)): # i is the number of rows
for j in range(len(ratings[i])): # j is the number of columns
print(ratings[i][j], end=" ") # Output: 4 5 6 7 8 9 12 1 10 11 3 2
Now, let’s see how you’ll find the average rating for the movie in 2nd column:
sum = 0
for row in range(len(ratings)):
sum += ratings[row][2]
print(sum / len(ratings)) # 7.0
Similarly, how do we increment each reviewer rating by 2:
for row in range(len(ratings)):
for column in range(len(ratings[row])):
ratings[row][column] += 2
print(ratings) # [[6, 7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 14, 3], [12, 13, 5, 4]]
Interview problem - How will you rotate a given matrix?
def rotateMatrix(matrix):
if not len(matrix):
return # return if matrix is empty
top = 0
bottom = len(matrix)-1
left = 0
right = len(matrix[0])-1
while left < right and top < bottom:
prev = matrix[top+1][left]
# Moving elements of top row one step right
for i in range(left, right + 1):
curr = matrix[top][i]
matrix[top][i] = prev
prev = curr
top += 1
# Moving elements of right column one step down
for i in range(top, bottom + 1):
curr = matrix[i][right]
matrix[i][right] = prev
prev = curr
right -= 1
# Moving elements of bottom one step left:
for i in range(right, left - 1, -1):
curr = matrix[bottom][i]
matrix[bottom][i] = prev
prev = curr
bottom -= 1
# Moving elements of leftmost column one step up
for i in range(bottom, top - 1, -1):
curr = matrix[i][left]
matrix[i][left] = prev
prev = curr
left += 1
return matrix
mat = [[4, 5, 6, 7], [8, 9, 12, 1], [10, 11, 3, 2]]
print(rotateMatrix(mat)) # [[8, 4, 5, 6], [10, 9, 12, 7], [11, 3, 2, 1]]
If you found this blog informative, please share.
tags: Python - DSA - CS